SteriLab™ provides a wide range of Microbiology testing services as per the principles of Good Microbiological Practices, Canadian Biosafety Standards,United States Pharmacopeia (USP), Association for the Advancement of Medical Instrumentation (AAMI), American National Standards Institute (ANSI) and Canadian Standard Association (CSA).
SteriLab™ test for bacteria, yeast and mold to ensure that the microbiological quality of your products and water samples is maintained in order to minimize the risk of potential infection.SteriLab™ Testing Services support the needs of a variety of industries and academic research institutes including medical device manufacturers, healthcare providers, food, pharmaceutical and personal care.
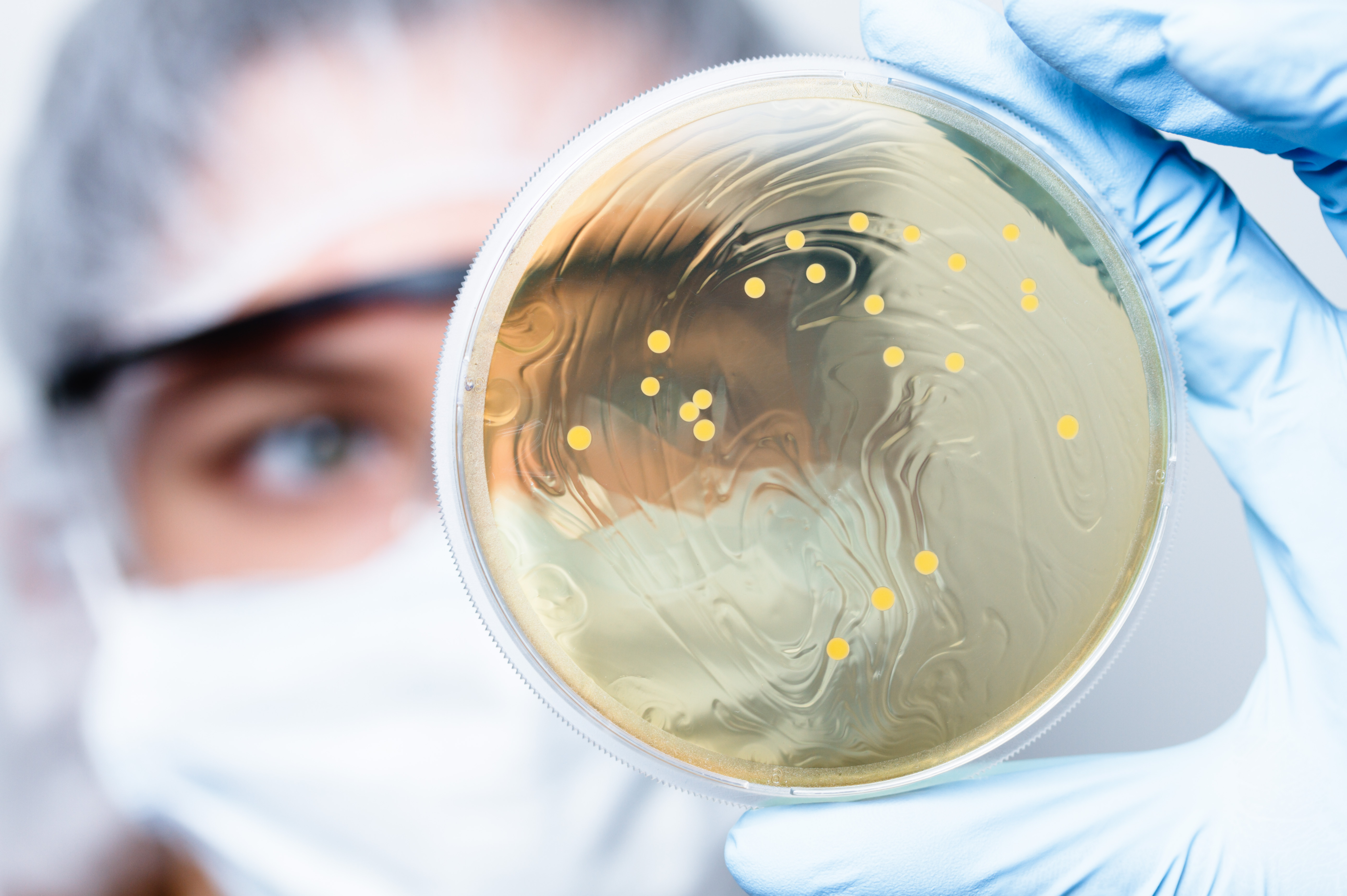

Sterility testing is performed as part of the validation of a sterilization process to determine the presence or absence of viable microorganisms on a product. Before performing the sterility test, a method suitability test (also called the bacteriostasis and fungistasis) shall be performed upon request to determine if the device or product has antimicrobial properties which may lead to false negative results during sterility testing.
Sterility testing will be performed using one of the following methods:
The appropriate incubation conditions will be employed for 14 days. Every effort must be made to carry out sterility test as quickly as possible after exposure to the sterilizing agent to prevent loss of viability of microorganisms.
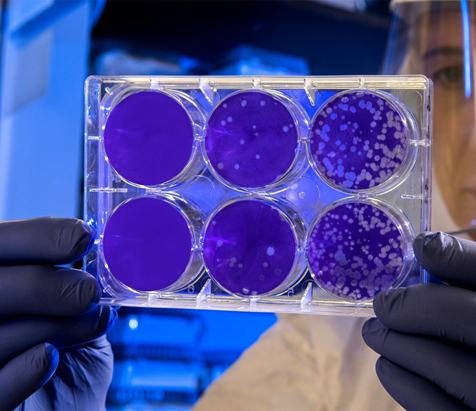

Product being tested for sterility should be screened to determine if any inhibitory substances are released into the medium as this may lead to false negative results. This is performed by the inoculation of low numbers of representative organisms into the medium containing the product.
Microbial identification is necessary when sterility tests result in positive findings. Bacteria responsible for food spoilage is commonly identified in food industry. Bacteria is also identified as part of antibiotic susceptibility testing in medical diagnostics or in a research setting. The first step in identification is to isolate a pure culture. Gram positive and Gram-negative bacteria are identified by performing Gram stain followed by a series of biochemical tests.

Bioburden testing determines the population of microorganisms on a medical device or other product.
Before performing the bioburden test, a bioburden method suitability shall be validated to demonstrate the product does not prevent the growth or detection of microorganisms and the adequacy of the technique for the removal and enumeration of microorganisms.
The methods of determination and microbial characterization of bioburden shall comprise of the following:
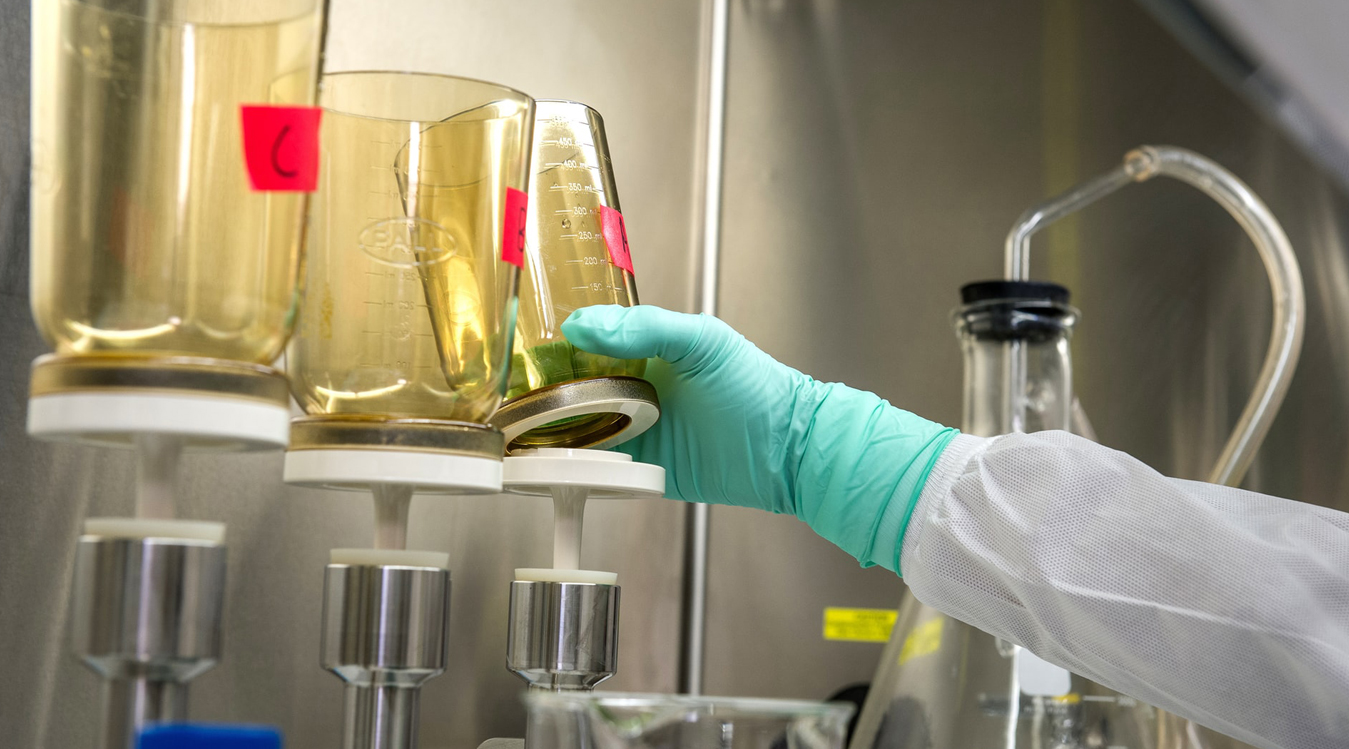

SteriLab™ performs microbial enumeration according to procedures outlined in USP <61>. Microbial Enumeration tests are usually performed on healthcare, pharmaceutical, laundry and cosmetic products ranging from raw materials to finished products.
The following methods are provided for TAMC and TYMC testing:
Antimicrobial agents or preservatives (if present in your sample) can inhibit the growth of microorganisms and could interfere with their detection. Neutralizing agents may be added to the chosen diluent or medium to neutralize the activity of antimicrobial agents.
Microbial colonies are counted and the microbial concentration is expressed as either Colony Forming Units, CFU/mL or CFU/g of tested sample.
USP <62> test evaluates a product for the presence or absence of potential pathogens in personal care products. USP <62> testing is performed to determine the presence of specified microorganisms: Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Escherichia coli, Salmonella species, Clostridia species, Candida albicans and bile-tolerant Gram-negative bacteria. The test involves an enrichment of the sample followed by transferring the sample onto selective agar media for determination of the presence or absence of specified microorganisms.
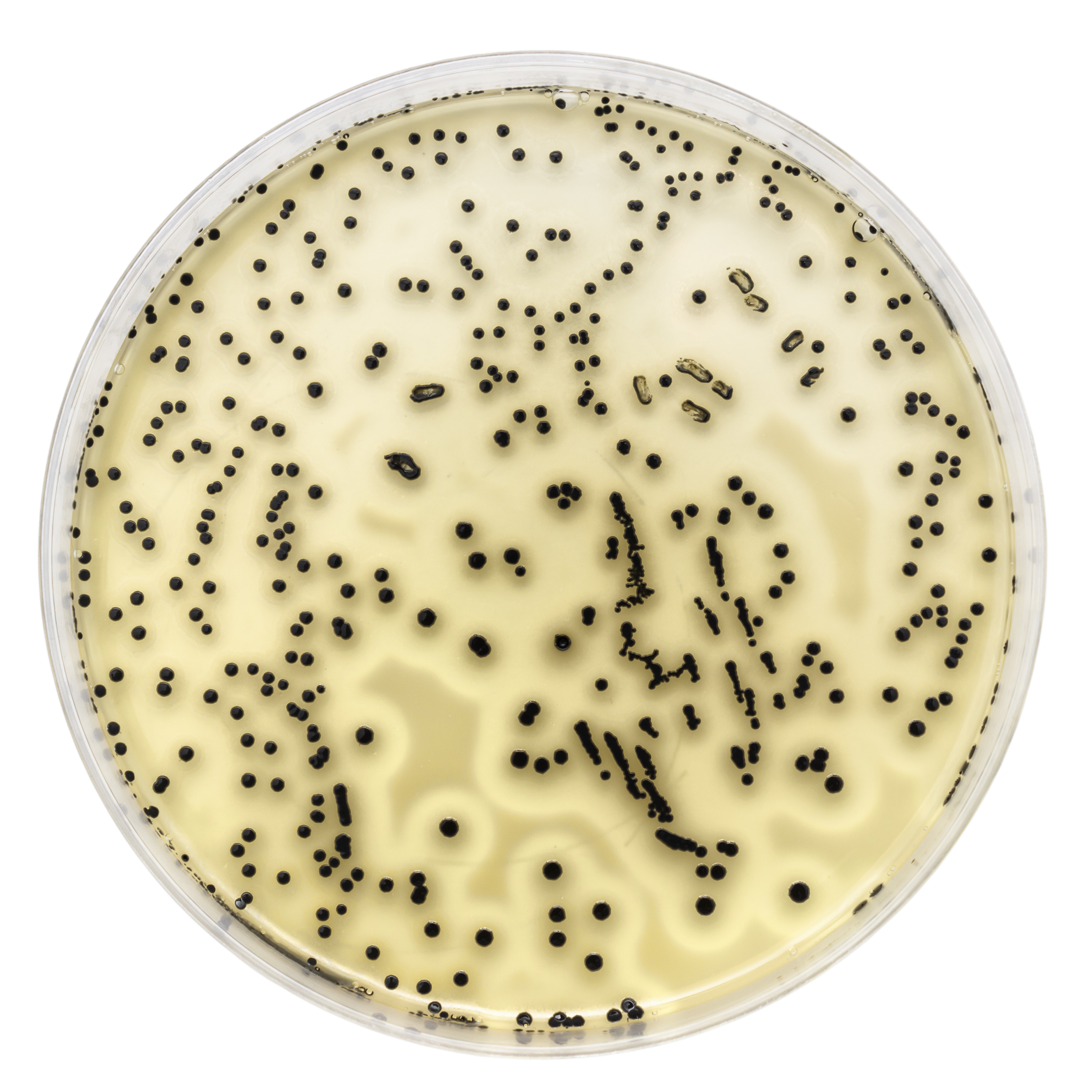
HPC is a procedure that estimates the number of viable bacteria that use organic molecules as their principal energy source. It can be used to determine the efficiency of a water treatment process and the quality of treated water.
The following method can be used to perform a heterotrophic plate count:

Bacterial endotoxins are lipopolysaccharides found on the outer membrane of Gram-negative bacteria and can cause a fever-like reaction and other adverse effects when introduced in the body. Unlike microorganisms, endotoxins are not reliably destroyed by disinfection or sterilization processes. Therefore, if the water used for reprocessing medical devices has high levels of endotoxins, residual endotoxins might remain on reprocessed devices.
Limulus amebocyte lysate (LAL) is an assay used for the detection and quantification of bacterial endotoxins. LAL assay is commonly performed as part of water quality testing.

USP <51> is used to evaluate the efficacy of antimicrobial preservatives used in consumer product including personal care, liquid laundry detergent and pharmaceutical. A challenge test consists of contaminating your product followed by an evaluation of the decrease in microbial load at defined intervals during a period of 28 days. USP <51> testing measures the effectiveness of antimicrobial preservatives against five microorganisms; Pseudomonas aeruginosa (ATCC 9027), Escherichia coli (ATCC 8739), Staphylococcus aureus (ATCC 6538), Candida albicans (ATCC 10231), Aspergillus brasiliensis (ATCC 16404).
Prior to initiation of USP <51>, SteriLab recommends testing the product for the presence of bacteria, yeast and mold as per USP <61>. Individual test samples and their respective positive controls are inoculated with each of the micro-organisms mentioned above. An aliquot of the samples is diluted in an appropriate neutralizer and plated at 0 day, 7 days, 14 days and 28 days. The number of microorganisms recovered from each time point are compared to those observed in the positive control at day 0. Changes in concentrations of microorganisms are expressed in terms of log reduction.

This test method is used to evaluate the antimicrobial efficacy of sanitizers on precleaned, inanimate, hard, nonporous, non-food contact surfaces against Staphylococcus aureus, or Klebsiella pneumoniae or Enterobacter aerogenes, or a combination thereof. The test is performed by contaminating test carriers with test micro-organisms followed by drying and exposing the product for desired contact time. The sample will then be plated and incubated. The number of surviving colonies will be compared to the control and the percent reduction will be determined.
For more information, please Contact Us.